CORPORATE TAX
IN DUBAI,
ABU DHABI &
THE UAE
Our Corporate Tax (CT) service in Dubai, Abu Dhabi and the UAE is part of our tax consultancy services in Dubai, Abu Dhabi and the UAE.
Corporate Tax is interchangeably referred to as Income Tax across the GCC countries. It is a form of direct tax collected by governments as a source of income; it is levied on the net income or profits of corporations and businesses.
The UAE government announced on 31 January 2022 their plan to introduce a federal Corporate Tax on business profits. With effect from 1 June 2023, Corporate Tax at a standard tax rate of 9% was applied to all mainland business and commercial activities on taxable profits above AED 375,000.
On 9 December 2022, the UAE released the Federal Decree-Law No. (47) of 2022 on the Taxation of Corporations and Businesses (hereinafter referred to as the ‘Corporate Tax Law’) which forms the basis for the implementation of the new Corporate Tax regime.

TIMING
Corporate Tax is effective for financial years starting on or after 1 June 2023. Businesses with an accounting reference date of 31 December will become subject to Corporate Tax from 1 January 2024.
FOREIGN TAX CREDITS
Any foreign Corporate Tax and Withholding Taxes (WHT) imposed on the UAE taxable income is allowed as a tax credit against the Corporate Tax liability.

TAX BASE
CT will be payable on the profits of the UAE businesses as reported in their financial statements prepared in accordance with accounting standards accepted in the UAE, with minimal exceptions and adjustments.

RATE
Corporate tax rates in the UAE follow a structured system: entities with taxable income up to AED 375,000 are exempt from corporate tax, while those with income exceeding this threshold face a 9% tax rate. Multinational corporations, falling under OECD Base Erosion and Profit-Sharing laws within Pillar 2 of the BEPS 2.0 framework, are subject to a 15% corporate tax rate, specifically if their combined worldwide revenues surpass AED 3.15 billion.
FREE ZONES
Businesses established in free zones are subject to Corporate Tax, but the Corporate Tax regime still continues to honour the Corporate Tax incentives currently being offered to free zone businesses that comply with all regulatory requirements and that do not conduct business with mainland UAE. Free zone businesses are required to register and file a Corporate Tax return. A Free Zone entity need audited financial statements if it wants to benefit from the 0% Corporate Tax regime for specific business activities.

ADMINISTRATION
The Federal Tax Authority (“FTA”) shall be responsible for the administration, collection, and enforcement of Corporate Tax. Businesses are required to register for Corporate Tax purposes and are required to electronically file one Corporate Tax return per financial period. No provisional or advance Corporate Tax filings is required, nor any advance Corporate Tax payments. A UAE group of companies may elect to form a tax group and be treated as a single taxable person (fiscal unity) if the parent company holds at least 95% of the share capital and voting rights of its subsidiaries. A UAE tax group is only required to file a single tax return for the entire group.
UAE CORPORATE TAX REGISTRATION PROCESS
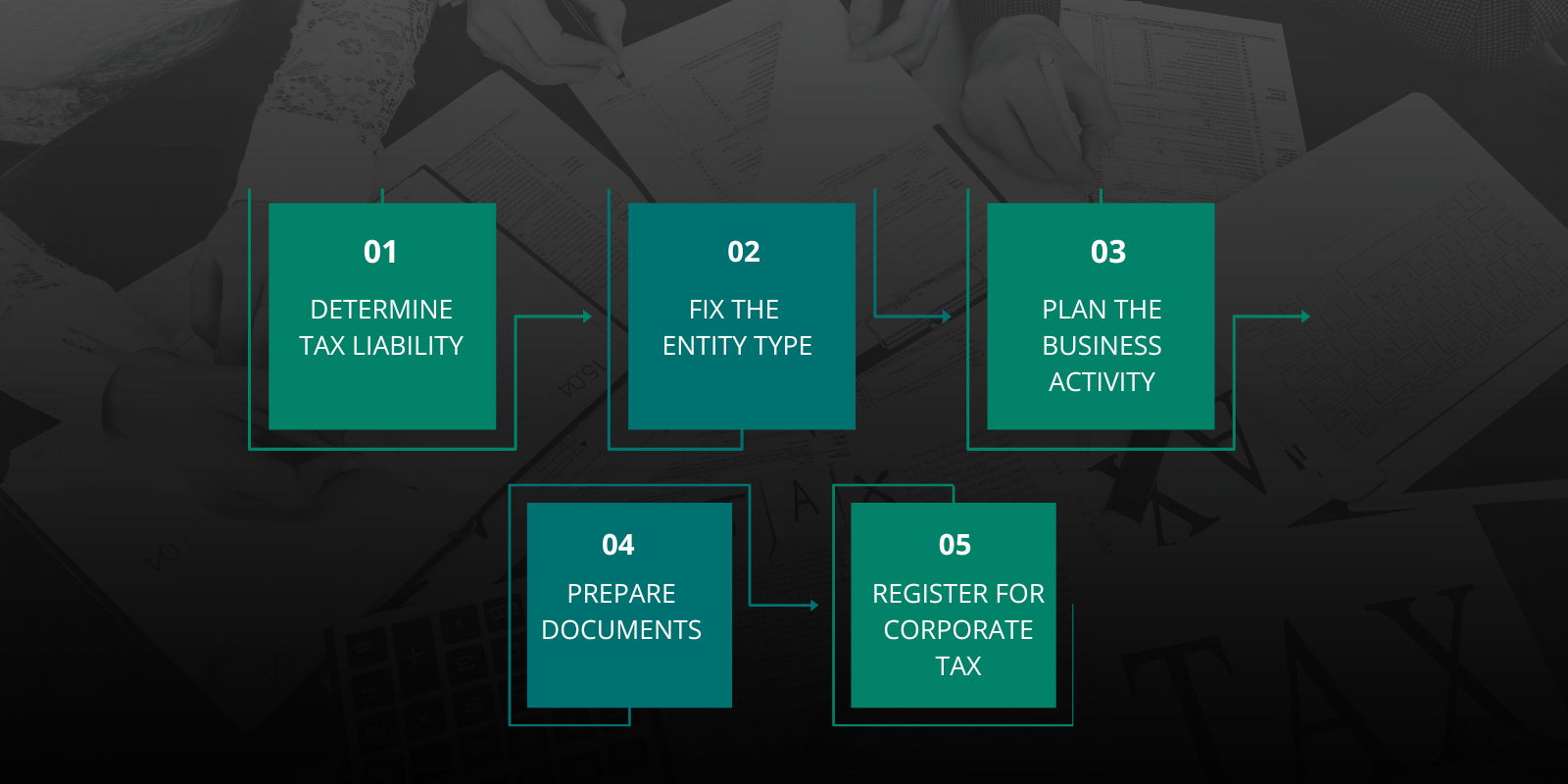
NAVIGATING UAE CORPORATE TAX AND ENSURING COMPLIANCE
To ensure compliance and mitigate risks, it is essential to seek professional guidance. Our team at Creation Business Consultants offers comprehensive support, including:
- Registration Assistance: We streamline the registration process and facilitate obtaining the necessary tax numbers for your business.
- Expert Consultation: Benefit from expert advice on tax planning, bookkeeping, financial statement preparation, and VAT and corporate tax filing.
- Timely Corporate Tax Registration: Any new business that has been established should ensure to register for corporate tax within three months of the company’s establishment/incorporation date.
Avoid the hefty penalty of AED 10,000 by registering for Corporate Tax promptly. Let’s collaborate to navigate the complexities of Corporate Tax, safeguarding your business’s financial health and reputation.
ACTIONS TO BE DONE BY BUSINESSES, SECURE YOUR FINANCIAL FUTURE
UAE businesses are strongly advised to prepare for the implementation of corporate tax. This may include the following:
- Performing an initial high level impact assessment to understand the potential tax effect of these changes on their business.
- Assessing whether the existing finance/tax function is sufficient.
- Training for finance and tax teams.
- Identifying potential restructuring opportunities.
- Review of contracting arrangements.
- Implementing changes to the existing legal structure.
- Changes to accounting systems.
The above information should hopefully help businesses understand the requirements and potential implications of these far-reaching tax changes in the UAE. Further information changes are expected.
WHAT ARE THE RISKS RELATED TO CORPORATE TAX SERVICES IN THE UAE?
Through careful planning and professional advice, the minimal risks connected to Taxes in the UAE can be reduced. You can handle the Tax legislations and procedures easily with the assistance of professional consultants, ensuring adherence to legislations and reducing potential risks.
For an expert consultation, contact Creation Business Consultants via email [email protected] or call +971 4 878 6240 today.
The Corporate Tax legislation (Federal Decree-Law No. 47 of 2022) by the UAE Ministry of Finance was released on 9 December 2022. Please see the link below for an overview of the Corporate Tax Law:
UAE CORPORATE TAX FAQs
The introduction of a competitive Corporate Tax system, aligned with international best practices, aims to solidify the UAE’s status as a premier global business and investment hub. This move supports the UAE’s development goals and strategic transformation. Additionally, it underscores the UAE’s dedication to adhering to global tax transparency standards and curbing harmful tax practices.
In the UAE, most businesses conducting commercial activities within the country are subject to corporate tax. This includes:
- Mainland companies: Businesses registered in any of the UAE’s emirates outside of a free zone.
- Branches of foreign companies: If a foreign company establishes a branch in the UAE mainland, it will be subject to corporate tax on its UAE-sourced profits.
Yes, UAE Corporate Tax applies uniformly to all entities, regardless of ownership. Juridical persons incorporated or resident in the UAE, and foreign entities with a Permanent Establishment or taxable nexus in the UAE, are subject to Corporate Tax, irrespective of the nationality or residence of their owners.
Certain UAE entities, such as government bodies and specific investment funds, can be exempt from UAE Corporate Tax. However, most business and commercial activities fall under its purview and corporate tax will apply.
The UAE Corporate Tax regime becomes effective for financial years starting on or after June 1, 2023.
Examples:
- If your business’s financial year begins on July 1, 2023, and ends on June 30, 2024, you will be subject to UAE Corporate Tax from July 1, 2023. This marks the start of the first financial year following June 1, 2023.
- For a business with a financial year starting on January 1, 2023, and ending on December 31, 2023, UAE Corporate Tax will apply from January 1, 2024. This aligns with the commencement of the first financial year following June 1, 2023.
Contact us for a free corporate tax consultation at [email protected] and avoid hefty fines for non- compliance.
Creation Business Consultants provides full support for corporate tax compliance and planning. Our services include assistance with corporate tax registration, filing, and structuring to help global companies minimize tax liabilities. We also offer expert consultation on tax planning, bookkeeping, financial statement preparation, and both VAT and corporate tax filing. Our goal is to ensure your business remains compliant and financially optimized in a rapidly evolving tax environment.
Yes, UAE Corporate Tax is a federal tax applicable across all Emirates, ensuring uniformity in tax regulations throughout the entire country.
Yes, natural persons engaged in business activities in the UAE, either directly or through partnerships or sole proprietorships, are subject to Corporate Tax.
The legal entity or natural person carrying out the business activity can register for corporate tax. Typically, each legal entity (company) is considered one Taxable Person.
The specific documents required may vary but generally include:
- Trade license
- Memorandum of Association (MOA)
- Financial statements
- Passport copies of owners/directors/Ultimate Beneficial Owners (UBO)
While the Federal Tax Authority (FTA) website and e-Services Portal are available in both English and Arabic, the registration process itself may require documents to be submitted in Arabic. Creation Business Consultants can ensure your documents are prepared correctly for a smooth registration experience. Contact us today for assistance at [email protected]
WHAT DATES AND ON WHEN SHOULD A COMPANY THAT HAS BEEN INCORPORATED REGISTER TO CORPORATE TAX IN UAE?
Companies are required to register for corporate tax within the timeframe specified by the Federal Tax Authority (FTA). This usually occurs within a month of beginning business activities.
Are you confused about the registration deadlines? Contact Creation Business Consultants at [email protected] for expert advice.
The Federal Tax Authority (FTA) aims to process registrations within twenty (20) business days upon submission of all required documents.
The tax return filing period depends on your company’s financial year. Generally, returns are due within the timeframe specified by the Federal Tax Authority (FTA), within a few months after the end of your financial year. Ensure you meet your filing deadlines for assistance reach out to [email protected] can help your business stay on top of its UAE corporate tax obligations.
The UAE follows the arm’s length principle for determining deductible expenses. This means expenses must be ordinary, necessary, wholly and exclusively incurred for the purpose of the business and incurred at arm’s length (fair market value) if dealing with related parties.
While there are no specific guidelines yet, common deductible expenses might include:
- Cost of goods sold
- Rent
- Salaries and wages
- Utilities
- Marketing and advertising expenses (up to a certain limit)
- Interest on business loans (with limitations)
Unsure about what expenses are deductible under UAE corporate tax? We can provide tailored advice based on your specific business activities. Reach out to [email protected] for more information and support.
Businesses are required to maintain sufficient records for at least five years from the end of the tax period to which the records relate. These records should support your tax calculations and disclosures in the return. This may include:
- Purchase and sales invoices
- Bank statements
- Accounting records
- Contracts
Keeping up with record-keeping requirements. For assistance with accounting, bookkeeping, tax and compliance advisory and services email [email protected] for your free initial consultation today!
No, Corporate Tax and VAT are distinct taxes, and both will be applicable in the UAE.
If your business is registered for VAT, you must pay both VAT and Corporate Tax separately. Non-VAT registered businesses may still be liable for Corporate Tax.
No, Corporate Tax and Excise Tax are separate taxes, both of which will continue to apply in the UAE.
Yes, applicable service fees will still be payable to the Federal or relevant Emirate Government. Business setup, license renewal, and other government fees incurred in the normal course of business are generally deductible for Corporate Tax purposes.
Yes, international agreements, including those for avoiding double taxation, must be considered under the UAE Corporate Tax regime. In cases of conflict between the Corporate Tax Law and an international agreement, the latter may limit the application of Corporate Tax.
“Business” and “Business Activity” refer to any economic activity, either ongoing or short-term, conducted by any person, typically with a profit motive and some system or organization. These terms are used in the Corporate Tax Law to determine when a person’s activities incur a UAE Corporate Tax liability. For businesses, all activities and assets are generally considered part of a “Business” for tax purposes. For natural persons, see the relevant FAQ about what constitutes a ‘Business or Business Activity’ for tax purposes. For personalized advice and more detailed information on UAE corporate tax, contact our tax experts at [email protected].
A Resident Person includes UAE-incorporated entities like Limited Liability Companies, Private and Public Joint Stock Companies, and other juridical persons. Natural persons conducting business in the UAE are also considered Resident Persons. Foreign entities may be treated as Resident Persons if they are effectively managed and controlled in the UAE, which can be indicated by where strategic decisions are made.
A Non-Resident Person is any juridical entity incorporated outside the UAE and managed outside the UAE. Natural persons who do not engage in taxable business activities in the UAE are also considered Non-Residents.
Resident juridical persons are taxed on their worldwide income, with certain exemptions for income earned through foreign subsidiaries and branches. Income from abroad that isn’t exempt is eligible for foreign tax credits to avoid double taxation.
Non-Residents are taxed only on income linked to their Permanent Establishment in the UAE, income with a UAE nexus as per Cabinet Decision No. 56 of 2023, and UAE-sourced income subject to a 0% Withholding Tax.
A Tax Period is the business’s Financial Year used for preparing financial statements, typically the Gregorian calendar year (1 January to 31 December). Businesses using a different 12-month period for financial statements will follow that period for their Tax Period.
The 0% rate applies to each Taxable Person’s total income up to AED 375,000, regardless of how many businesses they operate. Qualifying Free Zone Persons face a 9% rate on non-Qualifying Income. Multiple entities forming a Tax Group are considered one Taxable Person and share a single AED 375,000 threshold. Artificially splitting businesses to exploit the threshold can lead to penalties and income adjustments.
Taxable Income is calculated as the accounting net profit (or loss) reported under IFRS, adjusted for specific items like unrealized gains/losses, exempt income, intra-group transfers, restructuring gains/losses, non-deductible expenses, related party transactions, tax loss transfers, and other Minister-specified adjustments.
For personalized advice and more detailed information on UAE corporate tax, contact our tax experts at [email protected].
In the Corporate Tax Law, an individual is referred to as a “natural person.”
A natural person will be subject to UAE Corporate Tax when engaging in any Business or Business Activity with an annual turnover exceeding AED 1 million. However, income from employment, personal investments, and real estate investments is not considered a Business or Business Activity for tax purposes.
No, the Corporate Tax Law applies to natural persons with an annual turnover exceeding AED 1 million, irrespective of their citizenship or visa status.
A natural person’s taxable income includes all income derived from their Business or Business Activity in the UAE, including income earned from abroad related to that business or activity.
If a natural person conducts multiple Businesses or Business Activities, the combined turnover of all such activities will be considered when determining if the annual turnover exceeds the AED 1 million threshold.
No, employment income, including salaries, wages, allowances, and bonuses derived from an employment contract, is not subject to UAE Corporate Tax.
No, interest and other personal investment and savings income earned by a natural person in their personal capacity will not be subject to UAE Corporate Tax.
Personal Investment income includes income from investment activities conducted in a natural person’s personal capacity, such as interest or dividends. It does not include income from commercial businesses or activities requiring a license from a UAE Licensing Authority.
Real Estate Investment income refers to income earned from investment activities related to land or real estate property in the UAE, not requiring a license from a UAE Licensing Authority.
For personalized advice and more detailed information on UAE corporate tax, contact our tax experts at [email protected].
A “juridical person” is an entity established or recognized under UAE laws and regulations, or under foreign jurisdiction laws, possessing a legal personality distinct from its founders, owners, and directors. Examples include limited liability companies, foundations, ‘onshore’ trusts, public or private joint stock companies, and other entities with separate legal personalities under UAE mainland legislation or Free Zone regulations. UAE branches of domestic or foreign juridical persons are considered extensions of their parent or head office and do not have separate juridical status.
Having a separate legal personality means the entity holds its own rights, obligations, and liabilities. This generally limits the liability of the owners regarding the entity’s debts and obligations.
All activities conducted by a juridical person are considered “Business Activities” and fall within the scope of UAE Corporate Tax unless specifically exempted. For personalized advice and more detailed information on UAE corporate tax, contact our tax experts at [email protected].
Small Business Relief allows eligible businesses to be exempt from calculating and paying Corporate Tax and from adhering to regular Corporate Tax reporting requirements. If a business’s revenue is AED 3 million or below for the relevant tax period, it can elect to be treated as having no taxable income for that period, thus avoiding the need to file a full Corporate Tax return.
For tax periods ending on or before December 31, 2026, the following UAE Resident Persons with revenues of AED 3 million or less in the current and previous tax periods can claim Small Business Relief:
- Natural persons.
- Legal entities that are not:
- Constituent Companies of a Multinational Enterprise Group with total consolidated group revenue exceeding AED 3.15 billion.
- Qualifying Free Zone Persons.
If a business’s revenue exceeds AED 3 million in any tax period, it will no longer be eligible for Small Business Relief for that and future periods.
Yes, businesses with revenues of AED 3 million or less for the relevant and previous tax periods can apply for ‘Small Business Relief’ for tax periods ending on or before December 31, 2026.
If a business qualifies for Small Business Relief and its revenue is AED 3 million or below, it will be considered as having no taxable income, and no Corporate Tax will be payable.
For a business not eligible for Small Business Relief, the Corporate Tax liability on AED 1 million taxable income would be calculated as follows:
- Taxable Income up to AED 375,000: AED 375,000 x 0% = AED 0
- Taxable Income exceeding AED 375,000: (AED 1,000,000 – AED 375,000) = AED 625,000 x 9% = AED 56,250
Thus, the total Corporate Tax liability for the period would be AED 0 + AED 56,250 = AED 56,250.
For personalized advice and more detailed information on UAE corporate tax, contact our tax experts at [email protected].
Revenue refers to the total income derived during a tax period from various sources such as sales of goods and services, royalties, interest, premiums, and dividends, before deducting any costs or expenditures. For income from sales or services, it means the gross amount without subtracting the cost of goods sold or services.
















